New Congestion Mitigation and Air Quality Improvement Tools for Estimating Emissions Benefits of Highway and Intermodal Projects
The Congestion Mitigation and Air Quality Improvement (CMAQ) Program provides funding to state and local governments for transportation projects and programs in air quality nonattainment and maintenance areas to help meet the requirements of the Clean Air Act. CMAQ funded projects must demonstrate that they will provide emissions reductions.
Since 2015, the U.S. DOT Volpe Center has provided technical support to FHWA’s Office of Natural Environment in developing the CMAQ Emissions Calculator Toolkit, a suite of spreadsheet-based tools that helps agencies estimate emission benefits for eligible projects. The U.S. DOT Volpe Center’s expertise in emissions and congestion modeling and understanding of FHWA’s priorities and practices enables the development of easy-to-use tools for a wide range of stakeholders.
The CMAQ Toolkit currently includes 15 tools, covering more than 35 project types, including transit service expansion, electric vehicles and charging infrastructure, diesel retrofits, and bicycle and pedestrian improvements. In 2022, the U.S. DOT Volpe Center updated all tools in the CMAQ Toolkit to the latest version of the Environmental Protection Agency’s MOVES emissions model, MOVES3. In addition to updating base emissions and activity data, off-network idle (idling outside of the normal drive cycle, such as buses idling at stops or stations) and evaporative emissions were also incorporated into the CMAQ Toolkit.
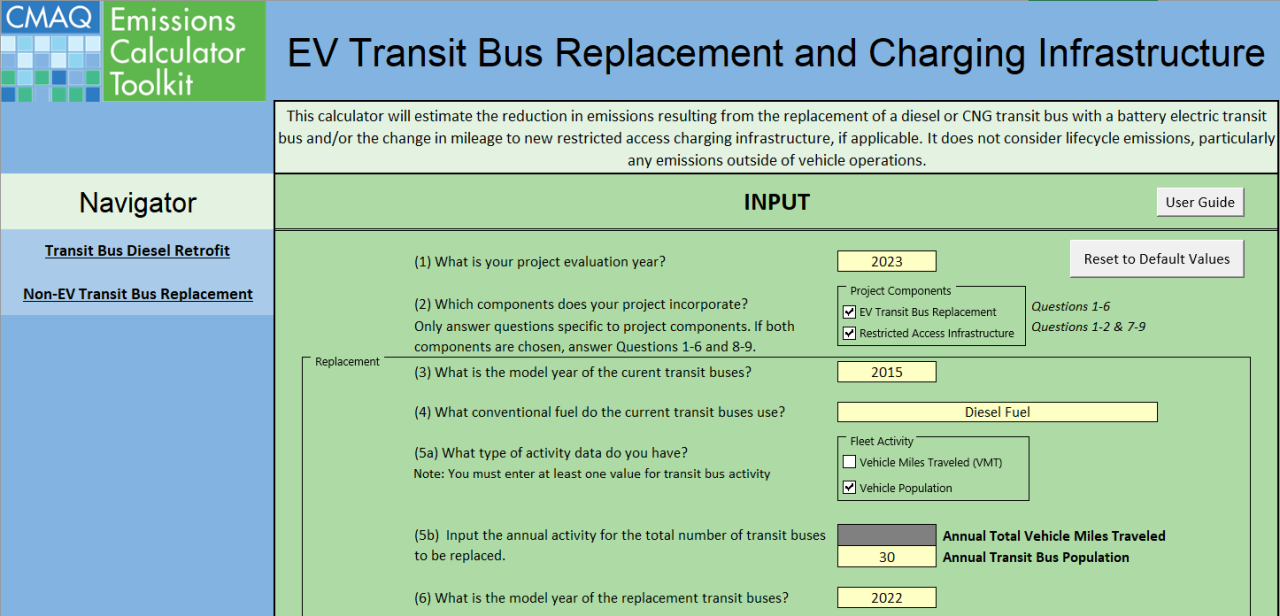
Electric vehicles and electrification projects have been a major focus area of CMAQ Toolkit development in 2022. The soon-to-be released Electric Vehicles and Charging Infrastructure tool estimates emissions benefits from purchase of electric municipal vehicle car and bus fleets and installation of restricted and unrestricted charging infrastructure. Emissions reductions are calculated based on upgrading diesel or gasoline vehicles to electric versions and building new charging stations along vehicle routes or near parking areas.
Other development efforts in 2022 have been concentrated on port and construction equipment and intermodal facilities. The Construction and Intermodal Equipment tool, released in April 2022, estimates emissions benefits from retrofitting non-road equipment, such as gantry cranes, drayage trucks, and tractors. The newest tool being developed, Intermodal Facilities and Projects, estimates the emission benefits from shifting freight movements (ton-miles or vehicle miles traveled) off highways and on to other modes, including rail and marine.
These two tools complement the Locomotive and Marine Retrofit and Replacement tool, released in November 2020, which models engine retrofits or repower/replacement for locomotives and marine vessels. All non-road equipment and intermodal tools include electric options, such as electric cranes and electric locomotives. Future tools updates will also incorporate shore power or “cold ironing,” which allows ships to connect to the local grid while in port.
Two new vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) and intelligent transportation systems (ITS) tools were also released recently: electronic and opening road tolling and travel advisories. V2I/ITS projects can improve air quality by smoothing the drive cycle of vehicles (i.e., lower emissions due to less stop-and-go and idling) and also help reduce traffic congestion.
Taken together, the new CMAQ tools will help transportation agencies quantify emissions benefits for a broader range of projects and expand the reach and consistency of the CMAQ program.
