Locomotive Emissions Comparison Tool for Rail Grant Applicants
The U.S. diesel locomotive fleet is dominated by older, highly polluting engines. FRA’s Consolidated Rail Infrastructure and Safety Improvements (CRISI) locomotive replacement initiative (LRI) facilitates upgrades to locomotive stock that meet or exceed Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) more stringent Tier 2, 3 and Tier 4 emissions standards. CRISI applicants are required to submit data on the estimated emission reduction benefits of their proposed projects. During the first year of the CRISI program in FY 2022, the LRI supported the replacement of 39 locomotives, including 15 new battery-electric locomotives. These locomotive replacement projects will significantly reduce toxic pollutant and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and reduce impacts on railyard workers and communities adjacent to yards.
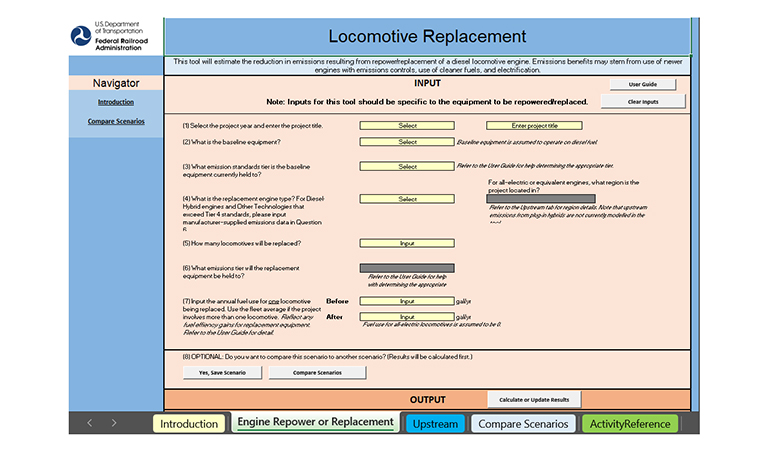
The Locomotive Emissions Comparison Tool (LECT) provides users with a standardized, easy-to-use approach to estimate emissions reductions for locomotive replacement projects being considered for funding under the CRISI grant program. The LECT outputs include estimated emissions reductions for three GHGs—CO2, CH4, and N2O—and five air pollutants—CO, NOx, PM2.5, PM10, and VOC. In addition to operational emission reductions, the tool also outputs emissions associated with diesel fuel extraction, production, and transport, and upstream emissions from electricity production. Both operational emissions (released in engine exhaust) and upstream emissions (released during fossil fuel or electricity production) are included in tool outputs. The LECT also allows users to save and compare locomotive replacement scenarios and sum emissions benefits across projects and arranges the information in an organized format. FRA recommends CRISI grant applicants use the tool not only for their application packet but also for their National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA)documentation.
The U.S. DOT Volpe Center was the lead developer of the LECT, working closely with FRA and its stakeholders in summer 2023 to design the Excel-based tool. The LECT was based on FHWA’s Congestion Mitigation and Air Quality (CMAQ) Emissions Calculator Toolkit, also developed by the U.S. DOT Volpe Center. A beta version of the LECT was tested by FRA staff and the California Air Resources Board (CARB) in September and October 2023, revised to incorporate beta tester feedback, and then published online in January 2024. Once the tool was published, the U.S. DOT Volpe Center team received additional feedback and minor bug fixes from railroads and CRISI grant applicants using the tool to estimate the emissions benefits of their projects.
The following example demonstrates emissions reductions from a typical locomotive replacement project involving switcher locomotives (switchers are used to assemble trains in railyards or make short transfer runs; they typically remain in service for a long time and are therefore older and more polluting than newer locomotives). A railyard operator proposes to replace three 1980s-era switchers, each typically consuming approximately 30,000 gallons of diesel fuel annually, with new electric battery-powered versions. LECT outputs show CO2 emissions reductions of over 950 metric tons per year for each of the three replacements. In context, a passenger vehicle emits approximately 4-5 metric tons of CO2 annually. Removing three old switcher locomotives from service equates to removing roughly 630 passenger vehicles from the road.
FRA’s Climate and Sustainability Program coordinates agency activities and initiatives that improve air quality, reduce GHG emissions, and promote the sustainability and resiliency of the rail network across multiple FRA offices. FRA is required by Executive Order 14057 to decarbonize and “green” its own actions and facilities. Data outputs from the LECT help FRA and U.S. DOT track progress toward reducing emissions from rail transport to achieve overall net zero transportation GHG emissions by 2050. Since many railyards are located in disadvantaged areas, the U.S. DOT Volpe Center’s efforts in LECT development also align with the White House’s Justice40 Initiative to reduce the disproportional environmental impacts of transportation on low-income and minority communities.
The U.S. DOT Volpe Center will conduct regular maintenance and updates to the tools for example, when new emissions data become available. The U.S. DOT Volpe Center also tracks suggested improvements and bug fixes submitted by tool users, including FRA grant applicants and grant recipients.
The LECT, user guide, and emissions data documentation are available on FRA’s website.
About the U.S. DOT Volpe Center
Celebrating more than 50 years of federal service to the nation, the U.S. DOT Volpe Center’s mission is to transform transportation for all.
We're Hiring: Learn more about our open job opportunities, our commitment to equity, and what it’s like to work at the U.S. DOT Volpe Center.
